Functions Library – Arma 3
Arma 3 Functions Library is pack of routine script functions available from anywhere in game. Main difference from older Functions Library is that it runs automatically and doesn't require Functions manager to be present.
Finding a Function
Before you can use a function, you first need to find it. The easies way is to access the Functions Viewer:
- In editor, click on
 icon or press Ctrl + F
icon or press Ctrl + F - In mission, access the debug console (automatically visible in pause menu of an editor mission) and click on FUNCTIONS button.
Once in the Functions Viewer, you can filter all available functions by location, projects and categories.
When you find the desired function, look at the code preview on the right. Every function has a header where you can find basic description of its functionality including required arguments, returned values and sometimes examples of use.
Calling a Function
Functions can be launched in mission, intro and outro using this call or spawn commands:
_returnedValue = arguments call functionName; arguments spawn functionName;
Arguments
Arguments are data sent into the function, affecting its behavior.
They can be mandatory or optional.
- Mandatory arguments are required for function to run. When missing, the function usually stops and throws an error.
- Optional arguments allows more detailed configuration. If you dont send them, the function will use pre-defined default values.
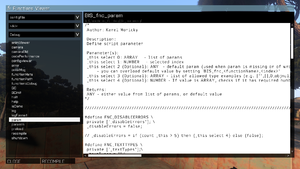
For example, let's take a look at BIS_fnc_endMission, a function which ends a mission with animated closing shot. This is what the header says:
/*
Author: Karel Moricky
Description:
Ends mission with specific ending.
Parameter(s):
0 (Optional):
STRING - end name (default: "end1")
ARRAY in format [endName,ID], will be composed to "endName_ID" string
1 (Optional): BOOL - true to end mission, false to fail mission (default: true)
2 (Optional):
BOOL - true for signature closing shot (default: true)
NUMBER - duration of a simple fade out to black
Returns:
BOOL
*/
As you can see, all arguments are marked optional and you can call the function without them.
[] call BIS_fnc_endMission;
- This will result in successfull ending of type "end1", preceeded with the signature closing shot.
["end2"] call BIS_fnc_endMission;
- Set the ending type to "end2", while keeping the other arguments intact.
["end2",false,false] call BIS_fnc_endMission;
- Fail the mission without any effect, using "end2" type.
However, what should you do if you want to set the only last argument without affecting the previous ones? The solution is simple - put an empty variable nil on their place.
[nil,nil,false] call BIS_fnc_endMission;
- Disable the closing effects, but keep the other aguments intact (successful "end1").
Returned Value
Functions executed by call command can return back a value. Let's take a look at BIS_fnc_sideName:
/*
Author: Karel Moricky
Description:
Returns side name
Parameter(s):
0: SIDE or NUMBER - either side or side ID
Returns:
STRING
*/
The function returns a String - localized name of a side.
_westName = west call BIS_fnc_sideName;
- Variable _westName will now be "BLUFOR" (or other name, based on selected language)
Multiplayer
Functions executed using call or spawn command will run only on the computer which triggered them. If you'd wish to execute a function remotely on specific clients, use BIS_fnc_MP function.
[arguments,"functionName",target,isPersistent] call BIS_fnc_MP;
User Interface
Anywhere outside of running mission, refer to the functions stored in uiNamespace.
arguments call (uiNamespace getVariable "functionName");
Adding a Function
When writing a script, consider registering it into the Functions Library.
Main benefits uncludes:
- Automatic compilation upon mission start into a global variable - no need to remember direct paths to files.
- Anti-hack protection using compileFinal
- Listing in the Functions Viewer
- Advanced debugging options
- Optional immediate execution upon mission start, without need for manual call
Mission
Mission specific functions can be configured in Description.ext.
Default Path
class CfgFunctions
{
class myTag
{
class myCategory
{
class myFunction {};
};
};
};
This will try to compile the function myTag_fnc_myFunction from the following file:
%MISSION_ROOT%\functions\myCategory\fn_myFunction.sqf
Customized Folder
You can customize the folder from which the functions will be loaded:
class CfgFunctions
{
class myTag
{
class myCategory
{
file = "myFolder";
class myFunction {};
};
};
};
This will try to compile the function myTag_fnc_myFunction from the following file:
%MISSION_ROOT%\myFolder\fn_myFunction.sqf
Customized File
Furthemore, you can set a specific file to be loaded:
class CfgFunctions
{
class myTag
{
class myCategory
{
class myFunction {file = "myFile.sqf";};
};
};
};
This will try to compile the function myTag_fnc_myFunction from the following file:
%MISSION_ROOT%\myFile.sqf
Addon
Writing a Function
WIP