Script File: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (→SQS syntax) |
Lou Montana (talk | contribs) m (Lou Montana moved page Script (File) to Script File: name standard) |
||
| (48 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
A | {{TOC|side}} | ||
A [[{{PAGENAME}}|script file]] is multiple commands and arguments defining wanted behaviour from the game, all grouped together in a textfile. This code does a specific task handled by the game engine. The common extensions for Arma scripts are '''.sqf''' and '''.sqs''', depending on the used syntax: [[SQF Syntax|SQF]] or (deprecated) [[SQS Syntax]]. | |||
{{Feature | Informative | See [[:Category:Community Tools#Code Edition|Community Tools - Code Edition]] for recommended text editors.}} | |||
== Syntax == | |||
In [[:Category:Operation Flashpoint|{{ofp}}]], scripts are limited to [[SQS Syntax]]. | |||
* See [[exec]] | |||
The already existing (since {{ofp}} v1.85) [[SQF Syntax]] was introduced for scripts in [[:Category:ArmA: Armed Assault|{{arma1}}]]. [[SQS Syntax]] is still usable but is considered deprecated since. | |||
* See [[execVM]], [[spawn]] | |||
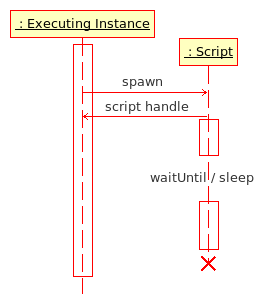
[[Image: Script_Execution.png|frame|right||Script Execution Diagram<br>'''Executing Instance:''' script, [[Function|function]] or game engine]] | |||
== Execution == | == Execution == | ||
| Line 19: | Line 21: | ||
* Other scripts | * Other scripts | ||
* Other [[Function|functions]] | * Other [[Function|functions]] | ||
* | * Init fields and (de)activation triggers in the [[Mission Editor]] | ||
* [[Event Handlers]] in addon config files | * [[:Category:Event Handlers|Event Handlers]] in addon config files | ||
The commands to execute scripts are: | |||
; | ; exec | ||
: [[exec]] starts a thread for a script in [[SQS Syntax]]. | |||
; execVM | |||
: [[execVM]] [[preprocessFileLineNumbers|preprocesses]] and [[compile|compiles]] a [[SQF Syntax]] script file and starts a thread for it. | |||
; call | |||
: [[call]] adds provided [[Code]] to the stack and wait for it to execute, then returns the code's last returned value. | |||
; | ; spawn | ||
: | : [[spawn]] starts a thread for provided [[Code]]. | ||
{{Feature | Informative | | |||
* [[execVM]] is almost like using {{ic|[[spawn]] [[compile]] [[preprocessFile]]}}. | |||
* [[spawn]] and [[execVM]] both add the thread to the [[Scheduler]] and provide a [[Script Handle|script handle]] which allows you to check if the spawned script is done (using [[scriptDone]]).}} | |||
== See also == | |||
* [[Function|Functions]] | |||
: | * [[:Category:Syntax|Syntax]] | ||
** [[SQF Syntax]] | |||
** [[SQS Syntax]] | |||
* [[Statement]] | |||
[[Category:Scripting Topics]] | [[Category:Scripting Topics]] | ||
Revision as of 19:18, 28 August 2021
A script file is multiple commands and arguments defining wanted behaviour from the game, all grouped together in a textfile. This code does a specific task handled by the game engine. The common extensions for Arma scripts are .sqf and .sqs, depending on the used syntax: SQF or (deprecated) SQS Syntax.
Syntax
In Operation Flashpoint, scripts are limited to SQS Syntax.
- See exec
The already existing (since Operation Flashpoint v1.85) SQF Syntax was introduced for scripts in Armed Assault. SQS Syntax is still usable but is considered deprecated since.

Script Execution Diagram
Executing Instance: script, function or game engine
Executing Instance: script, function or game engine
Execution
Scripts can be executed from several points in the game:
- Other scripts
- Other functions
- Init fields and (de)activation triggers in the Mission Editor
- Event Handlers in addon config files
The commands to execute scripts are:
- exec
- exec starts a thread for a script in SQS Syntax.
- execVM
- execVM preprocesses and compiles a SQF Syntax script file and starts a thread for it.
- call
- call adds provided Code to the stack and wait for it to execute, then returns the code's last returned value.