MaskMapper Tutorial for Visitor3: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 53: | Line 53: | ||
When the script is run, select your file to import, and then let Visitor do its thing. I have imported up to 1.2 million objects with success, but on my 6GB machine over that I can out of memory. If you import in lower batches, you can import many million. It is recommended you do break your file into many files, if doing large numbers of objects. | When the script is run, select your file to import, and then let Visitor do its thing. I have imported up to 1.2 million objects with success, but on my 6GB machine over that I can out of memory. If you import in lower batches, you can import many million. It is recommended you do break your file into many files, if doing large numbers of objects. | ||
==== Success! ==== | |||
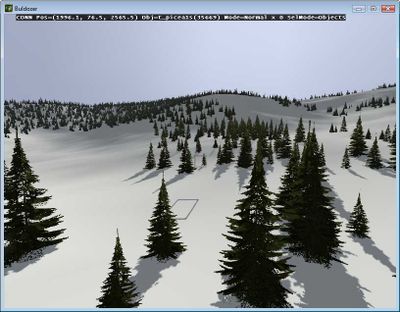
We successfully imported all the objects, and the results are below: | |||
[[Image:Maskmapper_visitor3_finish1.jpg|400px]] | |||
Revision as of 13:07, 15 November 2009
Outline
The purpose of this is to place large quantities of vegetation and other objects within certain areas of a map for ArmA/ArmA2. Previously, object placement was either via import from a previous map or manual placement. On most maps there may be as many as several hundred thousand individual objects, many of which are vegetation.
In this tutorial, we will take a "mask", and run that through a computer program that will generate objects randomly according to our specifications within that mask. This program will generate the output as a file that Visitor can read through its import process.
Instructions
We are going to input vegetation for this tutorial. Vegetation input is one of the last steps I take when preparing my map. In order to decide where you want the vegetation placed, you need to create a mask. This mask decides where vegetation will be placed and where it will not. It is similar, in principle, to masks used when spraypainting words on the side of containers.
Preparing your mask
To prepare a mask you need to either create the mask yourself in a program such as photoshop, or source it from GIS data. In this example I will be generating mine entirely from photoshop. I made an image of the "island" from Visitor 3, then imported this in photoshop, and painted the areas I wanted.
In preparing your mask, you need to pay special attention to the masks resolution. This means how much area each pixel of your mask is going to represent. Too higher resolution will take too long to process and reduce variation opportunities in your color range. Too low resolution will make the objects look placed within obvious sharp edged patterns. As a good rule of thumb, I have been using a mask that is either the same resolution as your height map, or half of that. So a resolution of between 5-10 meters per pixel is ideal. I do a seperate mask for each type of vegetation I wish to import. Sometimes running the same mask several times, if I have different types of a similar object (for example several variations of pines).
Creating the Mask
Here is my vegetation mask for Pines on my map alongside a the heightmap (provided for the sake of comparison):
- Dimensions of image must be square
- Image must be greyscale
Converting Mask to text
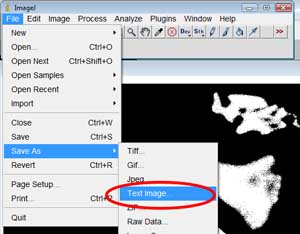
Download and install ImageJ, which is able to read BMP files and export them as Ascii Text. Open your mask within this, and then select "Save As" and "Text Image" as per the image below:
Using Mask Mapper
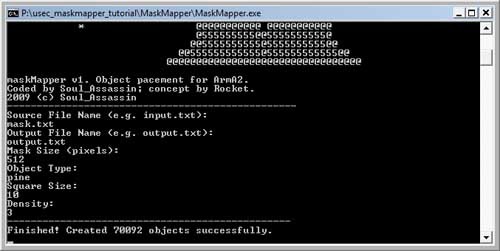
Our next step is to get MaskMapper to review your mask and prepare output for Visitor 3. Make sure you have installed MaskMapper, along with the required DLLs. Then run the program. The following arguments will be requested from you:
- Input File: The text file you exported from ImageJ.
- Output File: The name of the file to be outputed by MaskMapper.
- Mask Size (Pixels): The size of the mask in pixels.
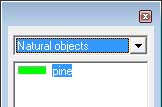
- Object Type: The type of object you are importing. This should be exactly the same (including case) as the name it has been given in Visitor 3.
- Square Size: This is the size covered by each pixel. In this case, as the mask is the same as the heightmap resolution, the value is the same (10m per square).
- Density: This is the amount of objects spawned when a value is 255 (maximum brightness). This is a linear scale for lower brightness, so if the pixel color is 120, the number of objects is Density x (120/255).
Importing into Visitor 3
This is your checklist before importing:
- Ensure you have your object named the same as you set during MaskMapper (this is VERY IMPORTANT!) and it is CASE SENSITIVE.
- Check your random orientation and size settings. These ARE used by the import script, so changing these will ensure your vegetation looks random.
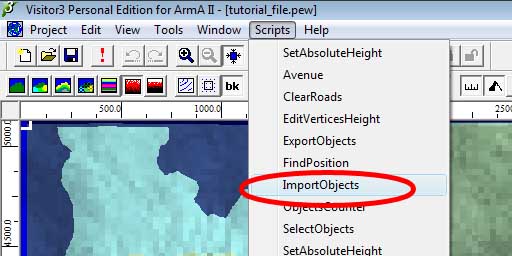
Open up visitor, and select the ImportObjects Script as shown below. Note: if you have not setup all the scripts, this menu you will be blank. You can find the ImportObjects.vis script in your Visitor 3 folder (usually c:\Program Files\Bohemia Interactive\Visitor 3\).
When the script is run, select your file to import, and then let Visitor do its thing. I have imported up to 1.2 million objects with success, but on my 6GB machine over that I can out of memory. If you import in lower batches, you can import many million. It is recommended you do break your file into many files, if doing large numbers of objects.
Success!
We successfully imported all the objects, and the results are below: