Creating an Addon – Arma 3
Lou Montana (talk | contribs) m (Fix link²) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 251: | Line 251: | ||
== Mod Folder Structure == | == Mod Folder Structure == | ||
The mod folder contents should be in a certain structure to be correctly recognized by the game, as well as when uploaded to the Steam Workshop.<br> | |||
The following tree list shows the general folder structure. Notice that some of these files/folders are optional, such as .bikey and .bisign files. | The following tree list shows the general folder structure. Notice that some of these files/folders are optional, such as .bikey and .bisign files. | ||
It is possible to ship other contents in the mod folder as well, such as documentation and changelog files. | It is possible to ship other contents in the mod folder as well, such as documentation and changelog files. | ||
Revision as of 21:12, 19 December 2024
This page explains the steps required to create an addon (PBO file).
Prerequisites
- An addon making tool such as:
- Arma 3 Tools
- Mikero's Tools
- HEMTT (GitHub)
- A text editor, such as Notepad++ or Visual Studio Code.
Preparing the Addon
Place all required files (scripts, textures, fonts, models, etc.) in an empty folder, which hereafter will be referred to as the Addon folder.
It is recommended to organize the files into subfolders to avoid clutter.
In order to make this addon fully functional, at least two additional steps are required, which are explained in further detail in the subsequent sections:
- A file named config.cpp should be created in the root of the Addon Folder for the game to be able to recognize the addon contents.
- Paths to all files in the addon, such as script paths, model paths, etc. should be adjusted with respect to the Addon Prefix.
Addon Prefix
In simple terms, Addon Prefix is a virtual (in-game) path to the root of an addon. This virtual path should be unique to prevent collision with other addons. The addon prefix is added to the PBO properties by the packing tool.
The addon prefix is typically a single word:
Addon_Name
It is also possible to use a directory-like structure, which is typically used by mods that contain several addons:
Mod_Name\Addon_Name\Category\...
For example:
My_Faction_Mod\Faction_Name\Vehicles
Once the addon prefix is set, the path to addon files will be as follows:
Addon_Prefix\Folder\File.format
For example, assume a file called car.p3d exists in the Addon Folder as follows:
Addon_Folder // Addon folder |__models // A folder in Addon Folder called "models" |__car.p3d // A p3d (3D model) file
Let's assume we've set the addon prefix to "My_Awesome_Car_Mod". In config.cpp, the model path should be:
model = "My_Awesome_Car_Mod\models\car.p3d";
Setting the Addon prefix
There are several ways to set the addon prefix, depending on the packing tool used. The instructions for two commonly used tools, namely Addon Builder and Mikero's Tools are explained.
Using Addon Builder
To set the addon prefix using Addon Builder, simply navigate to "Options" and modify the "Addon prefix" edit box.
Using Mikero's pboProject
To set the addon prefix using Mikero's pboProject, create a text file called $PBOPREFIX$.txt in the root of the addon folder, and type the addon prefix in the file.
Using HEMTT
To set the addon prefix using HEMTT, create a text file called $PBOPREFIX$ in the root of the addon folder, and type the addon prefix in the file. For more information on using HEMTT, see the "HEMTT Book".
Config.cpp
When the game loads an addon, it looks for a file called config.cpp to determine how to process the addon contents. Without such file, almost nothing will happen. In other words, config.cpp is the hub through which all of the addon contents (such as vehicles, weapons, sounds, functions, etc.) will be applied to the game.
This file should be created in the root of the Addon Folder. It is also possible to place additional config.cpp files in the subfolders of the addon, in which case the subfolders will be treated as separate addons by the game.
At the bare minimum, the config.cpp file requires a CfgPatches class. This will allow the game to determine what external addons are required by this addon, what objects/weapons are being added, as well as other information about the addon such as the author, version, etc.
All added/patched classes should be added to this file in order to be recognized and configured by the game.
Config Modifications
All added/modified config classes, such as CfgVehicles (objects, backpacks), CfgWeapons (weapons, weapon attachments, uniforms, vests, etc.), CfgMagazines (magazines, grenades, mines, etc.), CfgAmmo (projectiles, detonators, etc.), CfgFunctions (registered scripts), CfgCloudlets (particles), etc. need to be added to this file.
If the class contents are too long, it is recommended to put them in external files (e.g. CfgFunctions.hpp) and #include them in the config.cpp file:
// All addons must have this class
class CfgPatches
{
// ...
};
#include "cfgFunctions.hpp"
#include "some_other_file.hpp"
#include "ui\gui_defines.hpp"
// etc.
Scripts
Scripts can be executed through appropriate classes in config.cpp. There are several ways to execute scripts, depending on the time and place where it is supposed to happen.
For example, scripts that are to be executed at mission init can be added to the CfgFunctions class with an init flag, such as preInit = 1.
Scripts that need to execute when a certain event takes place can be executed using appropriate Event Handlers, if applicable. This method is typically used by vehicle/weapon event handlers.
Some community modifications, such as Community Base Addons 3 (CBA), add more ways to execute scripts, such as executing a script every time a unit is created (object init event handlers)
Signing the Addon (optional)
Signing an addon allows it to be used in multiplayer servers that check for addon signatures. To sign an addon, a private key is required.
Keys and Signatures
There are two types of keys: Private keys and Public keys.
Private Key
A private key is a file in .biprivatekey format. It is used to sign addons.
Public Key
A public key is a file in .bikey format. It is used by the server to check the addon signatures.
These files are safe to give to the public (typically published with the mod itself; see Mod Folder Structure).
Signature
A signature is a file placed next to the PBO file, to verify its contents.
They are named as addon_name.pbo.key_name.bisign
Creating the Keys
To create a key, use the DSUtils program in Arma 3 Tools.
Building the Addon
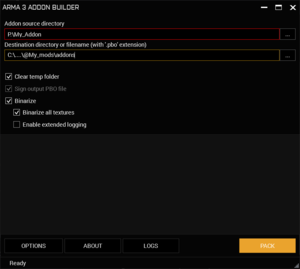
Addon Builder
Main interface
- Addon source directory: Should be the path to the Addon folder
- Destination directory or filename: The output folder which will contain the PBO file, as well as the signature (if "Sign output PBO" is checked)
- Sign Output PBO: See Signing the Addon
- Binarize: Binarized configs are loaded faster by the game. They will also be checked for syntax errors during the packing process.
Options
- List of files to copy directly: By default, only .cpp files are included in the addon. If other files need to be copied to the addon (e.g. scripts, models, etc.), add them to the list, separated by
- or ,. It is also possible to use the wildcard character * instead of the file names/formats. For example
*.p3d;*.paa;*.sqf;*.fxy;*.xml;*.bisurf;*.rvmat;*.h
All files will be copied in their original folder structure with respect to the Addon Folder.
- Addon Prefix: See Addon Prefix
- Path to private key file: Set this path to the private key file (if "Sign output PBO" is checked)
Other options can be left at their default values.
Finally, click on "Pack" to start the packing process.
Mikero's pboProject
HEMTT
HEMTT is a build system for addons. It has the great advantage of handling multiple addons at once as well as being able to be used in CLI environments like GitHub Actions. The Arma 3 Tools have to be installed for it to binarize files. After installing hemtt you can get information about the usage with hemtt help. For a basic setup follow these steps:
In the command line enter the following command:
hemtt init
If you get an error that hemtt was not found make sure that the executable is in the project folder or the hemtt directory is part of your %PATH% variable. Fill out the prompts. Then create a folder called "addons". Inside of this folder create another folder called "main". Then create the following files:
\z\prefix\addons\main
- config.cpp
#include "script_component.hpp"
class CfgPatches
{
class ADDON
{
name = CSTRING(component);
units[] = {};
weapons[] = {};
requiredVersion = REQUIRED_VERSION;
requiredAddons[] = { "CBA_main" };
author = "You";
url = "https://community.bistudio.com/wiki";
VERSION_CONFIG;
};
};
- script_component.hpp
#define COMPONENT main
#include "script_mod.hpp"
#ifdef DEBUG_ENABLED_MAIN
#define DEBUG_MODE_FULL
#endif
#ifdef DEBUG_SETTINGS_MAIN
#define DEBUG_SETTINGS DEBUG_SETTINGS_MAIN
#endif
#include "script_macros.hpp"
- script_mod.hpp
The MAINPREFIX defaults to "z", the PREFIX is the one you entered during setup.
#define MAINPREFIX z
#define PREFIX prefix
#include "script_version.hpp"
#define VERSION MAJOR.MINOR.PATCH
#define VERSION_AR MAJOR,MINOR,PATCH
#define REQUIRED_VERSION 1.88
- script_macros.hpp
This will add CBA as a dependency.
#include "\x\cba\addons\main\script_macros_common.hpp"
- script_version.hpp
Keep track of your mod's version in this file. Follows semantic versioning.
#define MAJOR 0
#define MINOR 0
#define PATCH 0
Now you should be able to run
hemtt build
The pbos are placed in the "addons" folder.
For more advanced setups and more examples check CBA's git repository as well as hemtt's GitHub page for documentation.
- Numbered list item
Mod Folder Structure
The mod folder contents should be in a certain structure to be correctly recognized by the game, as well as when uploaded to the Steam Workshop.
The following tree list shows the general folder structure. Notice that some of these files/folders are optional, such as .bikey and .bisign files.
It is possible to ship other contents in the mod folder as well, such as documentation and changelog files.
@My_Mod // Mod folder. The @ sign is not required, but it helps distinguish mods from official content. |__Addons // Addons folder, containing all addons and their signatures (if signed) | |__addon_name.pbo | |__addon_name.pbo.key_name.bisign | |__other_addon.pbo | |__other_addon.pbo.key_name.bisign | |__Keys // Keys folder (if the mod is signed) | |__key_name.bikey | |__mod.cpp // (Optional) mod.cpp contains the mod description, icon, hover icon, etc. |__mod.paa // (Optional) mod icon |__my_extension.dll // (Optional) extension that was created as part of the mod, if any |__my_mod_readme.pdf // (optional) Documentation file (not loaded by the game)