Script File: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
m (→Execution) |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
The commands to execute scripts are: | The commands to execute scripts are: | ||
* | * [[exec]] - used for scripts with [[SQS syntax]] | ||
* [[execVM]] - used for scripts with [[SQF syntax]] | |||
* [[spawn]] - used for scripts which were loaded with [[preprocessFile]] or [[loadFile]] | |||
* [[call]] - used for [[Function|functions]] which were loaded with [[preprocessFile]] or [[loadFile]] | |||
Scripts are running ''besides'' the executing instance. That means that the executing instance (f.i. script or [[Function|function]]) doesn't wait for the script to end. Thus scripts should not be used for code that should return a value, which is used in the calling script. This part is taken over by [[Function|functions]]. | Scripts are running ''besides'' the executing instance. That means that the executing instance (f.i. script or [[Function|function]]) doesn't wait for the script to end. Thus scripts should not be used for code that should return a value, which is used in the calling script. This part is taken over by [[Function|functions]]. | ||
Revision as of 01:30, 22 December 2006
A script is a chunk of code grouped together in a seperate textfile. This code does a specific task handled by the game engine. The common extensions for scripts are .sqs and .sqf, depending on the used syntax (see below). You can use any text editor like Notepad to edit scripts.
A special kind of a script is a function.
Usage
Scripts are mainly used for any game processes where timing is important. They are different to functions where the result or calculation is important.
Thus scripts can be used for cutscenes, dialogs, radio scripting and much more.
Syntax
In Operation Flashpoint, scripts are limited to SQS syntax.
In Armed Assault, the already existing SQF syntax was introduced for scripts. SQS syntax is still usable, but is considered deprecated in Armed Assault.
Execution
Scripts can be executed from several points in the game:
- Other scripts
- Other functions
- Scripting lines in the Mission Editor
- Event Handlers in addon config files
The commands to execute scripts are:
- exec - used for scripts with SQS syntax
- execVM - used for scripts with SQF syntax
- spawn - used for scripts which were loaded with preprocessFile or loadFile
- call - used for functions which were loaded with preprocessFile or loadFile
Scripts are running besides the executing instance. That means that the executing instance (f.i. script or function) doesn't wait for the script to end. Thus scripts should not be used for code that should return a value, which is used in the calling script. This part is taken over by functions.
Since Armed Assault, scripts return a script handle which you can use to verify whether a script is still running.
nserted from sqf syntax
With the release of Armed Assault, the SQS syntax for scripting was deprecated. SQF syntax is expected to be used for both scripts and functions.
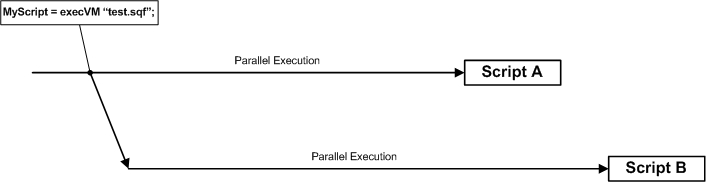
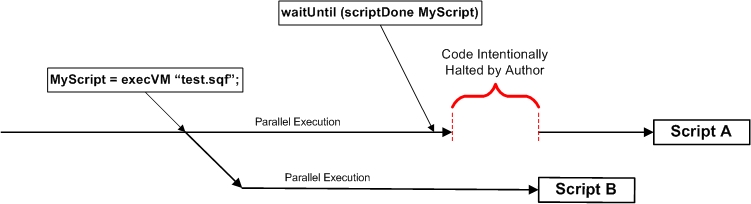
SQS syntax is compiled line-by-line as it is executed. SQF files must be compiled ahead of time and are thus more efficient at time of execution. SQF scripts are compiled and executed with either the execVM command or manually via compile and spawn. Since scripts run parallel with each other, you must use scriptDone if you wish to have a calling script wait for a called script to finish.
Diagram of Scripts Running in Parallel
Diagram of Scripts Running in Parallel using waitUntil and scriptDone to pause execution
Special Variables
_time in both syntax ?
Special Commands
Due to the fact, that calling instances aren't waiting for the scripts to end, scripts can be halted for a custom period of time. There are different methods to do this in SQF syntax (Armed Assault only) and SQS syntax (deprecated since Armed Assault).
SQF syntax
- Delay
- You can set the script to sleep for a number of seconds using the command sleep.
COMMAND 1; // wait 10 seconds sleep 10; COMMAND 2;
- Waiting for a condition
- You can set the script to sleep until a specific condition is met using the command waitUntil.
BOOL = false; // wait until BOOL gets true waitUntil BOOL; COMMAND;
SQS syntax
- Delay
- You can set the script to sleep for a number of seconds by introducing a line with ~, followed by the number of seconds.
COMMAND 1 ; wait 10 seconds ~10 COMMAND 2
- Waiting for a condition
- You can set the script to sleep until a condition is met by introducing a line with @, followed by the condition.
BOOL = false ; wait until BOOL gets true @BOOL COMMAND
- Waiting for a time
- You can set the script to sleep until a time (number of seconds since the beginning of the script) is met by introducing a line with &, followed by the time.
&100 ; is equivalent to @_time >= 100