Multiplayer Scripting: Difference between revisions
Lou Montana (talk | contribs) m (Fix a mixup of SP/MP commands) |
Lou Montana (talk | contribs) m (Text replacement - "{{arma3}} v1.57" to "{{arma3}} v1.58") |
||
| (72 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ | {{TOC|side|0.9}} | ||
This page aims to explain notions and specificities of [[Multiplayer Scripting]] and its differences with Singleplayer Scripting. | This page aims to explain notions and specificities of [[Multiplayer Scripting]] and its differences with Singleplayer Scripting.<br> | ||
It features three parts: | |||
# {{Link|#Notions and general knowledge}} | |||
# {{Link|#Structuring Multiplayer code}} | |||
# {{Link|#Testing locally|Testing locally}} | |||
= Notions and general knowledge = | |||
== The basics == | == The basics == | ||
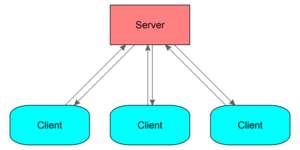
<div style="float: right">[[File:network client-server.png|thumb|Client-Server relationship]]</div> | |||
* In Multiplayer, players are connected to a '''server'''. | * In Multiplayer, players are connected to a '''server'''. | ||
** The server is a machine that distributes information among clients, such as unit positions, vehicle speeds, etc. | ** The server is a machine that distributes information among clients, such as unit positions, vehicle speeds, etc. | ||
** The server can be either a dedicated machine, or hosted by a player; in the latter it means the server can have a [[player]] unit. | ** The server can be either a dedicated machine, or hosted by a player; in the latter it means the server can have a [[player]] unit. | ||
* A machine connected to a server is called a '''client'''. | * A machine connected to a server is called a '''client'''. | ||
** Clients can join a mission ''after'' it started: they are considered " | ** Clients can join a mission ''after'' it started: they are considered "{{Link|#Join In Progress|JIP}}" and scripting should be adapted to them. See the {{Link|#Join In Progress}} chapter for more information. | ||
<br> | |||
{{ | {{Feature|informative|In Singleplayer, the game acts as a player-hosted server ([[isServer]] returns true).}} | ||
{{ | {{Feature|warning|Some Multiplayer commands do '''not''' work in Singleplayer, such as [[netId]]!<br> | ||
The other way around, some Singleplayer commands do not work in Multiplayer (e.g | The other way around, some Singleplayer commands do not work in Multiplayer (e.g [[setAccTime]]).}} | ||
| Line 21: | Line 29: | ||
=== Definitions === | === Definitions === | ||
* '''LOCAL''' is an attribute for the machine where the command/script/function is executed. | |||
* '''LOCAL''' is an attribute for the machine where the command/script/function is executed or the AI calculated. | |||
** to check if an argument is local, use the [[local]] command | ** to check if an argument is local, use the [[local]] command | ||
* '''REMOTE''' means '''non local'''. All player-controlled soldiers are remote units to a dedicated server, for example. | * '''REMOTE''' means '''non local''' - on another machine. All player-controlled soldiers are remote units to a dedicated server, for example. | ||
** to check if an argument is remote, simply use | ** to check if an argument is remote, simply use <sqf inline>not local _myObject</sqf> | ||
* [[:Category:Scripting_Commands|commands]] arguments and effects can be either '''local''' or '''global''': | * [[:Category:Scripting_Commands|commands]] arguments and effects can be either '''local''' or '''global''': | ||
{| | {| | ||
|style="padding-right: 0.5em;"|{{ | | style="padding-right: 0.5em;" | {{Icon|localArgument|32}} | ||
|a '''local''' argument means an argument that is processed on the machine where the command is executed | | a '''local''' argument means an argument that is processed on the machine where the command is executed | ||
|- | |||
| {{Icon|globalArgument|32}} | |||
| a '''global''' argument means any argument, even a remote one | |||
|- | |- | ||
|{{ | | {{Icon|localEffect|32}} | ||
|a ''' | | a '''local''' effect means that the effect will only happen on the machine where the command is executed | ||
|- | |- | ||
|{{ | | {{Icon|globalEffect|32}} | ||
|a ''' | | a '''global''' effect means that all the computers will receive it | ||
|- | |- | ||
|{{ | | {{Icon|serverExec|32}} | ||
| | | '''server exec''' means that the command or function has to be executed on the server machine, either mission host or dedicated server | ||
|} | |} | ||
See [[ | {{Feature|informative|See also: | ||
{{Columns|2| | |||
* [[:Category:Scripting Commands: Local Effect|Scripting Commands: Local Effect]] | |||
* [[:Category:Scripting Commands: Global Effect|Scripting Commands: Global Effect]] | |||
* [[:Category:Scripting Commands: Server Execution|Scripting Commands: Server Execution]] | |||
* [[:Category:Functions: Local Effect|Functions: Local Effect]] | |||
* [[:Category:Functions: Global Effect|Functions: Global Effect]] | |||
* [[:Category:Functions: Server Execution|Functions: Server Execution]] | |||
}} | |||
}} | |||
=== Different machines and how to target them === | |||
{{Feature|informative| | |||
* For obvious reasons, a server cannot be {{Link|#Join In Progress|JIP}}. | |||
* Use [[didJIP]] to determine if a client joined during the game. | |||
}} | |||
=== | {| class="wikitable valign-middle-row-1 align-center-col-2 align-center-col-3 align-center-col-4 align-center-col-5" | ||
! rowspan="2" | [[:Category:Scripting Commands|Scripting Commands]] | |||
! | ! colspan="2" | Server | ||
! | ! rowspan="2" | Player client | ||
! rowspan="2" | [[Arma 3: Headless Client|Headless client]] | |||
! rowspan="2" | Note | |||
|- | |||
! Dedicated | |||
! Player-Hosted | |||
|- | |||
| <sqf>isDedicated</sqf> | |||
| {{Icon|checked}} | |||
| {{Icon|unchecked}} | |||
| {{Icon|unchecked}} | |||
| {{Icon|unchecked}} | |||
| Dedicated server | |||
|- | |||
| <sqf>hasInterface && isServer</sqf> | |||
| {{Icon|unchecked}} | |||
| {{Icon|checked}} | |||
| {{Icon|unchecked}} | |||
| {{Icon|unchecked}} | |||
| Player server | |||
|- | |||
| <sqf>hasInterface && not isServer</sqf> | |||
| {{Icon|unchecked}} | |||
| {{Icon|unchecked}} | |||
| {{Icon|checked}} | |||
| {{Icon|unchecked}} | |||
| Player client | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | <sqf>not hasInterface && not isDedicated</sqf> | ||
|{{ | | {{Icon|unchecked}} | ||
| {{Icon|unchecked}} | |||
| {{Icon|unchecked}} | |||
| {{Icon|checked}} | |||
| Headless client | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | <sqf>isServer</sqf> | ||
|{{ | | {{Icon|checked}} | ||
| {{Icon|checked}} | |||
| {{Icon|unchecked}} | |||
| {{Icon|unchecked}} | |||
| Any server | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | <sqf>hasInterface</sqf> | ||
|{{ | | {{Icon|unchecked}} | ||
| {{Icon|checked}} | |||
| {{Icon|checked}} | |||
| {{Icon|unchecked}} | |||
| Any player | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | ! colspan="6" | Miscellaneous | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | <sqf>not isServer</sqf> | ||
|{{ | | {{Icon|unchecked}} | ||
| {{Icon|unchecked}} | |||
| {{Icon|checked}} | |||
| {{Icon|checked}} | |||
| All server clients, including headless clients, but excluding player host | |||
|- | |||
| <sqf>not isDedicated</sqf> | |||
| {{Icon|unchecked}} | |||
| {{Icon|checked}} | |||
| {{Icon|checked}} | |||
| {{Icon|checked}} | |||
| Everything but a dedicated server | |||
|- | |||
| <sqf>not hasInterface</sqf> | |||
| {{Icon|checked}} | |||
| {{Icon|unchecked}} | |||
| {{Icon|unchecked}} | |||
| {{Icon|checked}} | |||
| Headless clients and dedicated server | |||
|} | |} | ||
* If you want to know if the current machine is a server (Dedicated Server or Player Server), use | |||
* If you want to know if the current machine has a player (Player Server included), use {{ | '''For an extended version for all games, click''' <spoiler> | ||
{{ | {{Feature|informative|Before {{GVI|ofp|1.99}} and the backport of [[isServer]], the server could be identified by placing a [[Game Logic]] in the editor (that would always remain local to the server), then using the following: <sqf inline>local myLogic</sqf>.}} | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="line-height: normal; text-align: center" | |||
|- style="line-height: 2em" | |||
! Targeted machine | |||
! {{ofp}} | |||
! {{arma1}} | |||
! {{arma2}} | |||
! {{arma3}} | |||
|- | |||
! '''Dedicated Server'''<br><small>A server without a human player behind it</small> | |||
| <sqf>isServer && isNull player</sqf> | |||
| <sqf>isServer && isNull player</sqf> | |||
| <sqf>isDedicated</sqf> | |||
| <sqf>isDedicated</sqf> | |||
|- | |||
! '''Player Server'''<br><small>A server hosted by a player</small> | |||
| <sqf>isServer && not isNull player</sqf> | |||
| <sqf>isServer && not isNull player</sqf> | |||
| <sqf>isServer && not isDedicated</sqf> | |||
| <sqf>hasInterface && isServer</sqf> | |||
|- | |||
! '''Server'''<br><small>Any server, dedicated or hosted</small> | |||
| <sqf>isServer</sqf> | |||
| <sqf>isServer</sqf> | |||
| <sqf>isServer</sqf> | |||
| <sqf>isServer</sqf> | |||
|- | |||
! '''Player Client'''<br><small>A player connected since the lobby</small> | |||
| <sqf>not isServer && not isNull player</sqf> | |||
| <sqf>not isServer && not isNull player</sqf> | |||
| <sqf>not isServer && not isNull player</sqf> | |||
| <sqf>hasInterface && not isServer</sqf> | |||
|- | |||
! '''JIP Player Client'''<br><small>A player connected in the middle of a mission</small> | |||
| {{n/a}} | |||
| <sqf>not isServer && isNull player</sqf> | |||
| <sqf>not isServer && isNull player</sqf> | |||
| <sqf>hasInterface && didJIP</sqf> | |||
|- | |||
! '''Headless Client'''<br><small>A client without a human player behind it<br>(used to offload server calculations)</small> | |||
| colspan="3" {{n/a}} | |||
| <sqf>not hasInterface && not isServer</sqf> | |||
|- | |||
! '''JIP Headless Client'''<br><small>Headless client connected during the ongoing mission</small> | |||
| colspan="3" {{n/a}} | |||
| <sqf>not hasInterface && not isServer && didJIP</sqf> | |||
|} | |||
</spoiler> | |||
* If you want to know if the current machine is a server (Dedicated Server or Player Server), use [[isServer]]. | |||
* If you want to know if the current machine has a player (Player Server included), use [[hasInterface]]. | |||
{{Feature|arma3|Since {{arma3}}, a server-only init file is available: '''initServer.sqf''' (see [[Event Scripts]])}} | |||
{{Feature | arma3 | '''[[BIS_fnc_getNetMode]]''' can be used to have a string value representing the local machine status ("DedicatedServer", "Server", "HeadlessClient", "Client", "SinglePlayer" ).<br> | |||
This function doesn't make the JIP distinction and should be used along [[didJIP]].}} | |||
=== General information about locality === | === General information about locality === | ||
* about [[player]]: | * about [[player]]: | ||
** a [[player]]'s unit is '''always''' local to the (human) player's machine | ** a [[player]]'s unit is '''always''' local to the (human) player's machine | ||
** a dedicated server doesn't have a [[player]] unit ( | ** a dedicated server doesn't have a [[player]] unit (<sqf inline>isNull player</sqf> returns [[true]]) | ||
** to know if a certain unit is ''a'' player, use [[isPlayer]] | ** to know if a certain unit is ''a'' player, use [[isPlayer]] | ||
* groups and AI: | * groups and AI: | ||
| Line 75: | Line 215: | ||
* objects: | * objects: | ||
** a driven vehicle is always local to the machine of its driver (not the commander's, not the gunner's) | ** a driven vehicle is always local to the machine of its driver (not the commander's, not the gunner's) | ||
** terrain objects (buildings, vegetation, roads etc.) are local everywhere ( | ** terrain objects (buildings, vegetation, roads etc.) are local everywhere (<sqf inline>local nearestBuilding player</sqf> returns [[true]] on every client) | ||
** editor-placed objects and empty vehicles are local to the server | ** editor-placed objects and empty vehicles are local to the server | ||
** editor-placed '''triggers''' are created on every machine unless specified otherwise ("Server Only" [[Eden Editor]] option ticked) | ** editor-placed '''triggers''' are created on every machine unless specified otherwise ("Server Only" [[:Category:Eden Editor|Eden Editor]] option ticked) | ||
** units created with [[createUnit]] will be local to the computer that issued the command | ** units created with [[createUnit]] will be local to the computer that issued the command | ||
** objects and vehicles created with [[createVehicle]] will be local to the computer that issued the command | ** objects and vehicles created with [[createVehicle]] will be local to the computer that issued the command | ||
=== Locality changes === | === Locality changes === | ||
* if the player-leader dies, the AI is transferred to the machine where the new leader is local (server in case of AI, client in case of another player) | * if the player-leader dies, the AI is transferred to the machine where the new leader is local (server in case of AI, client in case of another player) | ||
* [[join|joining]] AI units will change locality to the new leader's computer | * [[join|joining]] AI units will change locality to the new leader's computer | ||
* locality will change from server to client when a player gets in an empty vehicle | * locality will change from server to client when a player gets in an empty vehicle | ||
* locality can also change in the event of a [[Team Switch]] or usage of [[selectPlayer]] | * locality can also change in the event of a [[Team Switch]] or usage of [[selectPlayer]] | ||
{{Feature|arma3|Since {{arma3}} the [[Arma 3: Event Handlers#Local|"Local" Event Handler]] triggers when an object's locality is changed.}} | |||
=== Code examples === | === Code examples === | ||
{|class=" | |||
!Code | {| class="wikitable" | ||
!Argu-ments | ! Code | ||
!Effect | ! Argu-ments | ||
!Description | ! Effect | ||
! Description | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | <sqf>remoteUnit setDamage 1;</sqf> | ||
|align="center"|{{ | | align="center" | {{Icon|globalArgument|32}} | ||
|align="center"|{{ | | align="center" | {{Icon|globalEffect|32}} | ||
|Any unit (local or remote) will die, and all the computers will know | | Any unit (local or remote) will die, and all the computers will know | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | <sqf>localUnit addMagazine "30Rnd_556x45_STANAG";</sqf> | ||
|align="center"|{{ | | align="center" | {{Icon|localArgument|32}} | ||
|align="center"|{{ | | align="center" | {{Icon|globalEffect|32}} | ||
|Only a local unit can have its inventory edited with this command, but all the machines will be notified: if a player looks into the ''localUnit'' inventory, the added magazine will be there | | Only a local unit can have its inventory edited with this command, but all the machines will be notified: if a player looks into the ''localUnit'' inventory, the added magazine will be there | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | <sqf>remoteUnit setFace "Miller";</sqf> | ||
|align="center"|{{ | | align="center" | {{Icon|globalArgument|32}} | ||
|align="center"|{{ | | align="center" | {{Icon|localEffect|32}} | ||
|Any unit (local or remote) can get its face changed, but the new face will not be propagated through the network. Only the local machine's player will see the effect of the command | | Any unit (local or remote) can get its face changed, but the new face will not be propagated through the network. Only the local machine's player will see the effect of the command | ||
{{ | {{Feature|informative|This command should ideally be '''executed on every machine''', for example with: | ||
<sqf>[remoteUnit, "Miller"] remoteExec ["setFace", 0, true];</sqf> | |||
See | See the {{Link|#Remote Execution}} chapter for more information.}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | <sqf>localCamera cameraEffect ["Internal", "Back"];</sqf> | ||
|align="center"|{{ | | align="center" | {{Icon|localArgument|32}} | ||
|align="center"|{{ | | align="center" | {{Icon|localEffect|32}} | ||
|Only a local camera can be entered, and of course only the local machine will see through this camera | | Only a local camera can be entered, and of course only the local machine will see through this camera | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 121: | Line 264: | ||
== Network ID == | == Network ID == | ||
Network IDs identify machines and network objects. They can be used to target proper machines with remote execution; see | Network IDs identify machines and network objects. They can be used to target proper machines with remote execution; see the {{Link|#Remote Execution}} chapter for more information. | ||
{{ | {{Feature|warning|'''A machine ID''' ([[owner|ownerID]]) is not to be confused with '''an object's network ID''' ([[netId]]).}} | ||
=== Machine network ID === | === Machine network ID === | ||
Every machine, including the server, has a '''network ID'''.<br | |||
A server has an ID of '''2''', every new client has the next number (the first client will be number '''3''', second client number '''4''', etc.) | Every machine, including the server, has a '''network ID'''.<br> | ||
A server always has an ID of '''2''', every new client has the next number (the first client will be number '''3''', second client number '''4''', etc.) | |||
* To get the current machine's ID, use [[clientOwner]]. | * To get the current machine's ID, use [[clientOwner]]. | ||
* To get the machine | * To get the machine ID of an object's owner, use [[owner]] ''object'' (MP only). | ||
* To get the machine | * To get the machine ID of a group's owner, use [[groupOwner]] ''object'' (MP only). | ||
{{ | |||
{{Feature|informative|'''0''' and '''1''' are special values: | |||
* '''0''' means '''everyone''' (including the server) | |||
* '''1''' means '''current machine''' but '''{{Color|darkred|is not implemented}}''' and should '''not''' be used.}} | |||
=== Object network ID === | |||
Every object synchronised through the network has a network ID, shortened to '''netId'''. | Every object synchronised through the network has a network ID, shortened to '''netId'''. | ||
* To get an object's netId, use [[netId]] (MP only). '''SP & MP variant:''' [[BIS_fnc_netId]] | * To get an object's netId, use [[netId]] (MP only). '''SP & MP variant:''' [[BIS_fnc_netId]] | ||
| Line 139: | Line 287: | ||
== PublicVariable commands == | == Sending information across network == | ||
=== Remote Execution === | |||
Since {{arma3}} v1.50, [[remoteExec]] and [[remoteExecCall]] efficient engine network commands are available: | |||
<sqf>"Message to everyone, including JIP players!" remoteExec ["hint", 0, true];</sqf> | |||
See [[Arma 3: Remote Execution]] for more information. | |||
{{arma3}} alpha introduced [[BIS_fnc_MP]] ('''obsolete''' since {{arma3}} v1.50, use the above version): | |||
<sqf>["Message to everyone, including JIP players!", "hint", true, true] call BIS_fnc_MP; // obsolete since Arma 3 v1.50, use remoteExec or remoteExecCall</sqf> | |||
{{arma2}} introduced the [[Arma 2: Multiplayer Framework]] (not present in {{arma3}}): | |||
<sqf> | |||
// having the Functions module placed in the editor | |||
waitUntil { not isNil "BIS_MPF_InitDone"; }; | |||
[nil, nil, rHINT, "Message to everyone!"] call RE; | |||
</sqf> | |||
=== PublicVariable commands === | |||
PublicVariable commands allow to send '''global''' variables to specified machines. | PublicVariable commands allow to send '''global''' variables to specified machines. | ||
| Line 145: | Line 311: | ||
* Short variable names should be used for network performance | * Short variable names should be used for network performance | ||
* These commands shouldn't be used intensely for the same reason | * These commands shouldn't be used intensely for the same reason | ||
{|class=" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
!Command | ! Command | ||
!Effect | ! Effect | ||
! {{Link|#Join In Progress|JIP}} synchronised | |||
|- | |- | ||
|[[publicVariable]] | | [[publicVariable]] | ||
|Set/update a variable value from the local machine to all the other machines (including server) | | Set/update a variable value from the local machine to all the other machines (including server) | ||
| align="center" | {{Icon|checked}} | |||
|- | |- | ||
|[[publicVariableServer]] | | [[publicVariableServer]] | ||
|Set/update a variable value '''from a client to the server''' | | Set/update a variable value '''from a client to the server''' | ||
| align="center" | {{Icon|unchecked}} | |||
|- | |- | ||
|[[publicVariableClient]] | | [[publicVariableClient]] | ||
|Set/update a variable value '''from the local machine''' (not necessarily the server) '''to a specific client''' | | Set/update a variable value '''from the local machine''' (not necessarily the server) '''to a specific client''' | ||
{{ | | align="center" | {{Icon|unchecked}} | ||
|} | |} | ||
=== How it works === | ==== How it works ==== | ||
The server has the variable {{ | The server has the variable {{hl|ABC_Score}} to broadcast: | ||
<sqf> | |||
ABC_Score = 5; // sets the value | |||
publicVariable "ABC_Score" // publishes the variable (do not forget the quotes!) | |||
</sqf> | |||
This sends the variable name and value to the clients. | This sends the variable name and value to the clients. | ||
* If the variable is not yet declared on their machine, it will declare it as well. | * If the variable is not yet declared on their machine, it will declare it as well. | ||
* If the variable already exists, '''the value is overridden''' by the server's value. | * If the variable already exists, '''the value is overridden''' by the server's value. | ||
* If the variable changes again on the server, it has to be manually [[publicVariable]]'d once again! | * If the variable changes again on the server, it has to be manually [[publicVariable]]'d once again! | ||
* A | * A {{Link|#Join In Progress|JIP}} player will synchronise '''server's''' [[publicVariable]]'d variables '''before''' executing '''init.sqf'''. See [[Initialisation Order]] for more information. | ||
** A JIP player will '''not''' synchronise [[publicVariableClient]]-received variables after he disconnects/reconnects. Only server-known public variables sent with [[publicVariable]] will be synchronised. | ** A JIP player will '''not''' synchronise [[publicVariableClient]]-received variables after he disconnects/reconnects. Only server-known public variables sent with [[publicVariable]] will be synchronised. | ||
=== setVariable command === | |||
Available since {{arma2}}, the '''public''' version of the [[setVariable]] command (alternative syntax) allows you to store a variable into an object and spread this variable across the network. | |||
{{Feature|arma3|In {{arma3}} it is possible to broadcast the [[nil]] value, thus deleting the variable from the target.}} | |||
{{arma2}} | |||
{{arma3}} | |||
== Player connection events == | |||
The following commands will execute given code when a player is connecting or disconnecting. This code will run for players connecting in the lobby '''and''' for {{Link|#Join In Progress|JIP}} players! | |||
* [[Arma 3: Mission Event Handlers#PlayerConnected|"PlayerConnected" mission Event Handler]] | |||
* [[Arma 3: Mission Event Handlers#PlayerDisconnected|"PlayerDisconnected" mission Event Handler]] | |||
{{Feature|informative|Before {{arma3}} v1.58, use [[BIS_fnc_addStackedEventHandler]] for [[onPlayerConnected]]/[[onPlayerDisconnected]].}} | |||
The following commands will execute given code when a player is connecting or disconnecting. This code will run for players connecting in the lobby '''and''' for | |||
* [[Arma 3: Event Handlers | |||
* [[Arma 3: Event Handlers | |||
{{ | |||
| Line 200: | Line 359: | ||
A client state is the client's connection state. It can be obtained with [[getClientState]] and [[getClientStateNumber]] commands on both server and clients. | A client state is the client's connection state. It can be obtained with [[getClientState]] and [[getClientStateNumber]] commands on both server and clients. | ||
{|class=" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
![[getClientStateNumber]] | ! [[getClientStateNumber]] | ||
![[getClientState]] | ! [[getClientState]] | ||
!Description | ! Description | ||
|- | |- | ||
|0 | | 0 | ||
|"NONE" | | "NONE" | ||
|No client (or singleplayer) | | No client (or singleplayer) | ||
|- | |- | ||
|1 | | 1 | ||
|"CREATED" | | "CREATED" | ||
|Client is created | | Client is created | ||
|- | |- | ||
|2 | | 2 | ||
|"CONNECTED" | | "CONNECTED" | ||
|Client is connected to server, message formats are registered | | Client is connected to server, message formats are registered | ||
|- | |- | ||
|3 | |3 | ||
|"LOGGED IN" | | "LOGGED IN" | ||
|Identity is created | | Identity is created | ||
|- | |- | ||
|4 | | 4 | ||
|"MISSION SELECTED" | | "MISSION SELECTED" | ||
|Mission is selected | | Mission is selected | ||
|- | |- | ||
|5 | | 5 | ||
|"MISSION ASKED" | | "MISSION ASKED" | ||
|Server was asked to send / not send mission | | Server was asked to send / not send mission | ||
|- | |- | ||
|6 | | 6 | ||
|"ROLE ASSIGNED" | | "ROLE ASSIGNED" | ||
|Role was assigned (and confirmed) | | Role was assigned (and confirmed) | ||
|- | |- | ||
|7 | | 7 | ||
|"MISSION RECEIVED" | | "MISSION RECEIVED" | ||
|Mission received | | Mission received | ||
|- | |- | ||
|8 | | 8 | ||
|"GAME LOADED" | | "GAME LOADED" | ||
|Island loaded, vehicles received | | Island loaded, vehicles received | ||
|- | |- | ||
|9 | | 9 | ||
|"BRIEFING SHOWN" | | "BRIEFING SHOWN" | ||
|Briefing was displayed | | Briefing was displayed | ||
|- | |- | ||
|10 | | 10 | ||
|"BRIEFING READ" | | "BRIEFING READ" | ||
|Ready to play mission | | Ready to play mission | ||
|- | |- | ||
|11 | | 11 | ||
|"GAME FINISHED" | | "GAME FINISHED" | ||
|Game was finished | | Game was finished | ||
|- | |- | ||
|12 | | 12 | ||
|"DEBRIEFING READ" | | "DEBRIEFING READ" | ||
|Debriefing read, ready to continue with next mission | | Debriefing read, ready to continue with next mission | ||
|} | |} | ||
{{ArgTitle|2|Join In Progress|{{GVI|arma1|1.00}}|{{GVI|ofpe|1.00}}}} | |||
'''Join In Progress''' (JIP) is the ability for a player to connect while a game is running, unlike in {{ofp}} where one had to wait for the game to be over.<br> | |||
{|class=" | It was introduced in [[:Category:{{ofpe}}|{{ofpe}}]] on Xbox and [[:Category:ArmA: Armed Assault|{{arma1}}]] on PC. | ||
!Information | |||
!Arma 1 | A player that joined in progress will be referred to as '''JIP player'''. | ||
!{{arma2}} | |||
!{{arma3}} | {{Feature | Informative | | ||
To disable JIP on a server: | |||
* the server admin can disable playable slots on the role selection screen | |||
* the mission designer can [[Description.ext#disabledAI|disable AI]] within mission config | |||
However, JIP remains available if respawn is enabled in the mission. | |||
}} | |||
=== JIP Synchronisation === | |||
A JIP player will have a lot of information synchronised ([[publicVariable]]'d and [[setVariable]] server variables for example) by the game '''before''' accessing the mission itself; see below: | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
! Information | |||
! Arma 1 | |||
! {{arma2}} | |||
! {{arma3}} | |||
|- | |- | ||
|date/time | | date/time | ||
|align="center"|{{ | | align="center" | {{Icon|checked}} | ||
|align="center"|{{ | | align="center" | {{Icon|checked}} | ||
|align="center"|{{ | | align="center" | {{Icon|checked}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
|date/time + [[setDate]]/[[skipTime]] | | date/time + [[setDate]]/[[skipTime]] | ||
|align="center"|{{ | | align="center" | {{Icon|unchecked}} | ||
|align="center"|{{ | | align="center" | {{Icon|unchecked}} | ||
|align="center"|{{ | | align="center" | {{Icon|checked}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
|weather ([[overcast]], [[fog]]) | | weather ([[overcast]], [[fog]]) | ||
|align="center"|{{ | | align="center" | {{Icon|unchecked}} | ||
|align="center"|{{ | | align="center" | {{Icon|checked}} | ||
|align="center"|{{ | | align="center" | {{Icon|checked}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
|weather + [[setOvercast]]/[[setFog]]/[[setRain]]/[[setLightnings]] | | weather + [[setOvercast]]/[[setFog]]/[[setRain]]/[[setLightnings]] | ||
|align="center"|{{ | | align="center" | {{Icon|unchecked}} | ||
|align="center"|{{ | | align="center" | {{Icon|unchecked}} | ||
|align="center"|{{ | | align="center" | {{Icon|checked}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
|time passed since mission start ([[time]] command) | | time passed since mission start ([[time]] command) | ||
|align="center"|''unknown'' | | align="center" | ''unknown'' | ||
|align="center"|''unknown'' | | align="center" | ''unknown'' | ||
|align="center"|{{ | | align="center" | {{Icon|checked}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[publicVariable]]-sent variables ([[Number]], [[String]], [[Text]], [[Array]], [[Code]]) | | [[publicVariable]]-sent variables ([[Number]], [[String]], [[Structured Text]], [[Array]], [[Code]]) | ||
|align="center"|{{ | | align="center" | {{Icon|checked}} | ||
|align="center"|{{ | | align="center" | {{Icon|checked}} | ||
|align="center"|{{ | | align="center" | {{Icon|checked}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[publicVariable]]-sent variables ([[nil]]) | | [[publicVariable]]-sent variables ([[nil]]) | ||
|align="center"|{{ | | align="center" | {{Icon|unchecked}} | ||
|align="center"|{{ | | align="center" | {{Icon|unchecked}} | ||
|align="center"|{{ | | align="center" | {{Icon|checked}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[setVariable]]-assigned variables (when alternative syntax's ''public'' parameter is set to true) | | [[setVariable]]-assigned variables (when alternative syntax's ''public'' parameter is set to true) | ||
| | | {{n/a}} | ||
|align="center"|{{ | | align="center" | {{Icon|checked}} | ||
|align="center"|{{ | | align="center" | {{Icon|checked}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[remoteExec]]- and [[remoteExecCall]]-executed code if ''JIP'' prerequisites are met | | [[remoteExec]]- and [[remoteExecCall]]-executed code if ''JIP'' prerequisites are met | ||
| | | colspan="2" {{n/a}} | ||
| align="center" | {{Icon|checked}} | |||
|align="center"|{{ | |||
|} | |} | ||
See [[ | |||
{{Feature|warning|All the '''initialisation fields''' code get executed again for '''each and every JIP connecting player'''.<br> | |||
This means that code with global effect {{Icon|globalEffect|32}} (such as [[setDamage]]) '''WILL''' be re-executed (depending on locality)!}} | |||
=== Related Commands === | |||
* [[remoteExec]] | |||
* [[remoteExecCall]] | |||
* [[didJIP]] | |||
* [[didJIPOwner]] | |||
* [[exportJIPMessages]] | |||
* [[isRemoteExecutedJIP]] | |||
== See also == | |||
* [[Arma 3: Headless Client|Headless Client]] | |||
* [[Initialisation Order]] | |||
* [[Arma 3: Remote Execution]] | |||
= Structuring Multiplayer code = | |||
== Responsibilities == | |||
* The '''server''' initialises and works with '''variables''' | |||
* A connecting or connected '''player-client''' gets the mission data from the server | |||
* Once an objective is reached, '''the server tells the players''' ''via'' [[remoteExec]]/[[remoteExecCall]], [[publicVariable]] or [[setVariable]] | |||
* Players can get their client-side UI code triggered by the server | |||
See {{Link|#Different machines and how to target them|this earlier chapter}} to know how to target specific machines. | |||
=== Server === | |||
The '''Server''' must be considered as the one ruler of the mission. He is the game's referee and all the decisions should come from it. All the values on the server should be considered as '''true'''.<br> | |||
Consider the server as a powerful machine where you can put all the mission conditions and heavy scripting on. | |||
In case of a very heavy mission, the server can be assisted by [[Arma 3: Headless Client|Headless Clients]] (this involves a per-mission specific design). | |||
Server-side code must gather or wait all the variables (potentially from client-side scripts and [[publicVariableServer]]) and take and broadcast its decisions accordingly using [[publicVariable]]. | |||
Server-side code should ideally '''not''' make any reference to a [[player]] variable considering a server can potentially be '''dedicated''', unless you want to force this mission to be player-hosted (such as {{arma2}}'s campaign). | |||
{{Feature|informative|Use [[allPlayers]], [[BIS_fnc_listPlayers]], [[playableUnits]] (and [[switchableUnits]] for SP compatibility) to refer to players.}} | |||
=== Client === | |||
The '''Client''' must be considered as an average machine that can leave the game at any moment. | |||
'''No mission-vital code must be executed on its side''' and '''no decisions must be taken client-side'''.<br> | |||
Again, '''one must expect that any client can disconnect at any moment'''. | |||
The client executes all the (local) UI code ([[Post Process Effects]], [[Arma: GUI Configuration|Dialogs]], etc.)<br> | |||
The player's machine should not deal with a great piece of code. | |||
{{Feature | important | Do not forget that a server '''can''' be a player, and therefore should execute player code in that case.}} | |||
The proper way to check for player-side condition is | |||
<sqf>if (hasInterface) then { /* (...) */ };</sqf> | |||
Note that the following example is '''incorrect''': | |||
<sqf> | |||
if (isServer) then | |||
{ | |||
// ... | |||
} | |||
else // WRONG: a server CAN be a player | |||
{ | |||
// ... | |||
}; | |||
</sqf> | |||
== Code writing == | |||
The usual four steps of coding are the following: | |||
* Think it well | |||
** If you cannot figure out how to write your code, say what you want to do out loud or write it down in your language, then replace it by code little by little. | |||
* Make it work | |||
** use the [[Arma 3: Startup Parameters#Developer Options|-showScriptErrors]] startup parameter to see your code errors. | |||
* Make it readable | |||
** name your variables properly, as if you had to give it to someone that should get it without the need of explaining | |||
* Optimise then | |||
** use more performance-friendly commands, reduce your search radius and loop frequencies once everything works. | |||
See {{Link|Code Optimisation#Rules}} for advices and more information. | |||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
* [[Arma 3 Headless Client|Headless Client]] | * [[Event Scripts]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Code Optimisation]] | ||
* [[: | |||
** [[:Category: | |||
* [[ | = Local Multiplayer Testing = | ||
* [[Arma 3 | |||
To ensure all cases, your mission should ideally work properly: | |||
* in Singleplayer | |||
* in Player-hosted Multiplayer | |||
* in a Dedicated Server-hosted game | |||
The following chapters explain how to mimic multiple clients on one computer. Of course, nothing prevents you from inviting friends to play your mission and report bugs! | |||
== Dedicated Server == | |||
To properly test MP scripting locality issues, it is recommended to run a '''dedicated server''' and connect with '''two''' clients. In order to do so: | |||
* In your server executable's [[Arma 3: Server Config File|server.cfg]]: <syntaxhighlight lang="cpp"> | |||
loopback = true; // force LAN-only server | |||
kickDuplicate = 0; // disable duplicate Arma kick | |||
// needed in case of Headless Client test only | |||
headlessClients[] = { "127.0.0.1" }; | |||
localClient[] = { "127.0.0.1" }; | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
* Run the game twice from Steam and connect each (with {{hl|-showScriptErrors}} flag) | |||
** If you use one screen for the first client and the other screen for the second client, use {{hl|-noPause -window}} launcher options. This will not pause render if the window doesn't have focus.<!-- | |||
-->{{Feature|important |Be sure to disable [[BattlEye]] or it will close any additional instances.}} | |||
* Try your mission and check for script errors: | |||
** on client's screens and [[arma.RPT|RPT files]] | |||
** in your server's [[arma.RPT|RPT files]] | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
! Pros | |||
! Cons | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
* Tests almost all "can go wrong" scenarios | |||
* Can test [[Arma 3: Headless Client|Headless Clients]], persistent server, server restart, admin login/logout | |||
| | |||
* Misses cases where [[isDedicated]] is used instead of [[isServer]] | |||
* "Big" setup | |||
|} | |||
== Player-Hosted Server == | |||
While this method covers less cases than the {{Link|#Dedicated Server Test}} method above, this method is faster: | |||
* Open the [[Arma 3: Launcher]] and disable [[BattlEye]] | |||
* Select the mods that the host will use (if any) | |||
* Launch the game using the {{hl|Play}}/{{hl|Play with Mods}} button | |||
* Select the mods that clients will use | |||
* Launch the game again using the {{hl|Play}}/{{hl|Play with Mods}} button | |||
* In the first game instance (server), host the mission either through local hosting or with [[:Category:Eden Editor|Eden Editor]] MP mission type launch | |||
* In the second game instance (client), join the session using the MP tab LAN section and entering the mission hosted by the server | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
! Pros | |||
! Cons | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
* Fast setup (with quick modlist support) | |||
* Helps find cases where [[isDedicated]] is used instead of [[isServer]] | |||
| | |||
* May miss locality issues (code that happens to run on the server because it runs on the server's ''client'' like e.g [[hideObjectGlobal]]) | |||
* No headless client testing (this can be solved by using a custom [[Arma 3: Server Config File|server.cfg]]) | |||
|} | |||
== See Also == | |||
* [[Arma 3: Dedicated Server]] | |||
* [[Arma 3: Server Config File|server config]] | |||
[[Category: Scripting | [[Category:Arma Scripting Tutorials]] | ||
Latest revision as of 19:22, 15 September 2024
This page aims to explain notions and specificities of Multiplayer Scripting and its differences with Singleplayer Scripting.
It features three parts:
Notions and general knowledge
The basics
- In Multiplayer, players are connected to a server.
- The server is a machine that distributes information among clients, such as unit positions, vehicle speeds, etc.
- The server can be either a dedicated machine, or hosted by a player; in the latter it means the server can have a player unit.
- A machine connected to a server is called a client.
- Clients can join a mission after it started: they are considered "JIP" and scripting should be adapted to them. See the Join In Progress chapter for more information.
Locality
Definitions
- LOCAL is an attribute for the machine where the command/script/function is executed or the AI calculated.
- to check if an argument is local, use the local command
- REMOTE means non local - on another machine. All player-controlled soldiers are remote units to a dedicated server, for example.
- commands arguments and effects can be either local or global:
| LALocal | a local argument means an argument that is processed on the machine where the command is executed |
| GAGlobal | a global argument means any argument, even a remote one |
| LELocal | a local effect means that the effect will only happen on the machine where the command is executed |
| GEGlobal | a global effect means that all the computers will receive it |
| SEServer | server exec means that the command or function has to be executed on the server machine, either mission host or dedicated server |
Different machines and how to target them
| Scripting Commands | Server | Player client | Headless client | Note | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dedicated | Player-Hosted | ||||
| Dedicated server | |||||
| Player server | |||||
| Player client | |||||
| Headless client | |||||
| Any server | |||||
| Any player | |||||
| Miscellaneous | |||||
| All server clients, including headless clients, but excluding player host | |||||
| Everything but a dedicated server | |||||
| Headless clients and dedicated server | |||||
For an extended version for all games, click
| Targeted machine | Operation Flashpoint | Armed Assault | Arma 2 | Arma 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dedicated Server A server without a human player behind it |
||||
| Player Server A server hosted by a player |
||||
| Server Any server, dedicated or hosted |
||||
| Player Client A player connected since the lobby |
||||
| JIP Player Client A player connected in the middle of a mission |
N/A | |||
| Headless Client A client without a human player behind it (used to offload server calculations) |
N/A | |||
| JIP Headless Client Headless client connected during the ongoing mission |
N/A | |||
- If you want to know if the current machine is a server (Dedicated Server or Player Server), use isServer.
- If you want to know if the current machine has a player (Player Server included), use hasInterface.
General information about locality
- about player:
- groups and AI:
- an AI group with a player-leader will be local to the player's computer
- a subordinate player being in a player-lead group will remain local to its computer (see bulletpoint #1)
- objects:
- a driven vehicle is always local to the machine of its driver (not the commander's, not the gunner's)
- terrain objects (buildings, vegetation, roads etc.) are local everywhere (local nearestBuilding player returns true on every client)
- editor-placed objects and empty vehicles are local to the server
- editor-placed triggers are created on every machine unless specified otherwise ("Server Only" Eden Editor option ticked)
- units created with createUnit will be local to the computer that issued the command
- objects and vehicles created with createVehicle will be local to the computer that issued the command
Locality changes
- if the player-leader dies, the AI is transferred to the machine where the new leader is local (server in case of AI, client in case of another player)
- joining AI units will change locality to the new leader's computer
- locality will change from server to client when a player gets in an empty vehicle
- locality can also change in the event of a Team Switch or usage of selectPlayer
Code examples
| Code | Argu-ments | Effect | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| GAGlobal | GEGlobal | Any unit (local or remote) will die, and all the computers will know | |
| LALocal | GEGlobal | Only a local unit can have its inventory edited with this command, but all the machines will be notified: if a player looks into the localUnit inventory, the added magazine will be there | |
| GAGlobal | LELocal | Any unit (local or remote) can get its face changed, but the new face will not be propagated through the network. Only the local machine's player will see the effect of the command | |
| LALocal | LELocal | Only a local camera can be entered, and of course only the local machine will see through this camera |
Network ID
Network IDs identify machines and network objects. They can be used to target proper machines with remote execution; see the Remote Execution chapter for more information.
Machine network ID
Every machine, including the server, has a network ID.
A server always has an ID of 2, every new client has the next number (the first client will be number 3, second client number 4, etc.)
- To get the current machine's ID, use clientOwner.
- To get the machine ID of an object's owner, use owner object (MP only).
- To get the machine ID of a group's owner, use groupOwner object (MP only).
Object network ID
Every object synchronised through the network has a network ID, shortened to netId.
- To get an object's netId, use netId (MP only). SP & MP variant: BIS_fnc_netId
- To get an object from a netId, use objectFromNetId (MP only). SP & MP variant: BIS_fnc_objectFromNetId
- To get a group from a netId, use groupFromNetId (MP only). SP & MP variant: BIS_fnc_groupFromNetId
Sending information across network
Remote Execution
Since Arma 3 v1.50, remoteExec and remoteExecCall efficient engine network commands are available:
See Arma 3: Remote Execution for more information.
Arma 3 alpha introduced BIS_fnc_MP (obsolete since Arma 3 v1.50, use the above version):
Arma 2 introduced the Arma 2: Multiplayer Framework (not present in Arma 3):
PublicVariable commands
PublicVariable commands allow to send global variables to specified machines.
- Network reception is guaranteed
- Short variable names should be used for network performance
- These commands shouldn't be used intensely for the same reason
| Command | Effect | JIP synchronised |
|---|---|---|
| publicVariable | Set/update a variable value from the local machine to all the other machines (including server) | |
| publicVariableServer | Set/update a variable value from a client to the server | |
| publicVariableClient | Set/update a variable value from the local machine (not necessarily the server) to a specific client |
How it works
The server has the variable ABC_Score to broadcast:
This sends the variable name and value to the clients.
- If the variable is not yet declared on their machine, it will declare it as well.
- If the variable already exists, the value is overridden by the server's value.
- If the variable changes again on the server, it has to be manually publicVariable'd once again!
- A JIP player will synchronise server's publicVariable'd variables before executing init.sqf. See Initialisation Order for more information.
- A JIP player will not synchronise publicVariableClient-received variables after he disconnects/reconnects. Only server-known public variables sent with publicVariable will be synchronised.
setVariable command
Available since Arma 2, the public version of the setVariable command (alternative syntax) allows you to store a variable into an object and spread this variable across the network.
Player connection events
The following commands will execute given code when a player is connecting or disconnecting. This code will run for players connecting in the lobby and for JIP players!
Client state
A client state is the client's connection state. It can be obtained with getClientState and getClientStateNumber commands on both server and clients.
| getClientStateNumber | getClientState | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | "NONE" | No client (or singleplayer) |
| 1 | "CREATED" | Client is created |
| 2 | "CONNECTED" | Client is connected to server, message formats are registered |
| 3 | "LOGGED IN" | Identity is created |
| 4 | "MISSION SELECTED" | Mission is selected |
| 5 | "MISSION ASKED" | Server was asked to send / not send mission |
| 6 | "ROLE ASSIGNED" | Role was assigned (and confirmed) |
| 7 | "MISSION RECEIVED" | Mission received |
| 8 | "GAME LOADED" | Island loaded, vehicles received |
| 9 | "BRIEFING SHOWN" | Briefing was displayed |
| 10 | "BRIEFING READ" | Ready to play mission |
| 11 | "GAME FINISHED" | Game was finished |
| 12 | "DEBRIEFING READ" | Debriefing read, ready to continue with next mission |
Join In Progress (JIP) is the ability for a player to connect while a game is running, unlike in Operation Flashpoint where one had to wait for the game to be over.
It was introduced in Operation Flashpoint: Elite on Xbox and Armed Assault on PC.
A player that joined in progress will be referred to as JIP player.
JIP Synchronisation
A JIP player will have a lot of information synchronised (publicVariable'd and setVariable server variables for example) by the game before accessing the mission itself; see below:
| Information | Arma 1 | Arma 2 | Arma 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| date/time | |||
| date/time + setDate/skipTime | |||
| weather (overcast, fog) | |||
| weather + setOvercast/setFog/setRain/setLightnings | |||
| time passed since mission start (time command) | unknown | unknown | |
| publicVariable-sent variables (Number, String, Structured Text, Array, Code) | |||
| publicVariable-sent variables (nil) | |||
| setVariable-assigned variables (when alternative syntax's public parameter is set to true) | N/A | ||
| remoteExec- and remoteExecCall-executed code if JIP prerequisites are met | N/A | ||
Related Commands
See also
Structuring Multiplayer code
Responsibilities
- The server initialises and works with variables
- A connecting or connected player-client gets the mission data from the server
- Once an objective is reached, the server tells the players via remoteExec/remoteExecCall, publicVariable or setVariable
- Players can get their client-side UI code triggered by the server
See this earlier chapter to know how to target specific machines.
Server
The Server must be considered as the one ruler of the mission. He is the game's referee and all the decisions should come from it. All the values on the server should be considered as true.
Consider the server as a powerful machine where you can put all the mission conditions and heavy scripting on.
In case of a very heavy mission, the server can be assisted by Headless Clients (this involves a per-mission specific design).
Server-side code must gather or wait all the variables (potentially from client-side scripts and publicVariableServer) and take and broadcast its decisions accordingly using publicVariable.
Server-side code should ideally not make any reference to a player variable considering a server can potentially be dedicated, unless you want to force this mission to be player-hosted (such as Arma 2's campaign).
Client
The Client must be considered as an average machine that can leave the game at any moment.
No mission-vital code must be executed on its side and no decisions must be taken client-side.
Again, one must expect that any client can disconnect at any moment.
The client executes all the (local) UI code (Post Process Effects, Dialogs, etc.)
The player's machine should not deal with a great piece of code.
The proper way to check for player-side condition is
Note that the following example is incorrect:
Code writing
The usual four steps of coding are the following:
- Think it well
- If you cannot figure out how to write your code, say what you want to do out loud or write it down in your language, then replace it by code little by little.
- Make it work
- use the -showScriptErrors startup parameter to see your code errors.
- Make it readable
- name your variables properly, as if you had to give it to someone that should get it without the need of explaining
- Optimise then
- use more performance-friendly commands, reduce your search radius and loop frequencies once everything works.
See Code Optimisation - Rules for advices and more information.
See also
Local Multiplayer Testing
To ensure all cases, your mission should ideally work properly:
- in Singleplayer
- in Player-hosted Multiplayer
- in a Dedicated Server-hosted game
The following chapters explain how to mimic multiple clients on one computer. Of course, nothing prevents you from inviting friends to play your mission and report bugs!
Dedicated Server
To properly test MP scripting locality issues, it is recommended to run a dedicated server and connect with two clients. In order to do so:
- In your server executable's server.cfg:
loopback = true; // force LAN-only server kickDuplicate = 0; // disable duplicate Arma kick // needed in case of Headless Client test only headlessClients[] = { "127.0.0.1" }; localClient[] = { "127.0.0.1" };
- Run the game twice from Steam and connect each (with -showScriptErrors flag)
- If you use one screen for the first client and the other screen for the second client, use -noPause -window launcher options. This will not pause render if the window doesn't have focus.
- Try your mission and check for script errors:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
Player-Hosted Server
While this method covers less cases than the Dedicated Server Test method above, this method is faster:
- Open the Arma 3: Launcher and disable BattlEye
- Select the mods that the host will use (if any)
- Launch the game using the Play/Play with Mods button
- Select the mods that clients will use
- Launch the game again using the Play/Play with Mods button
- In the first game instance (server), host the mission either through local hosting or with Eden Editor MP mission type launch
- In the second game instance (client), join the session using the MP tab LAN section and entering the mission hosted by the server
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|